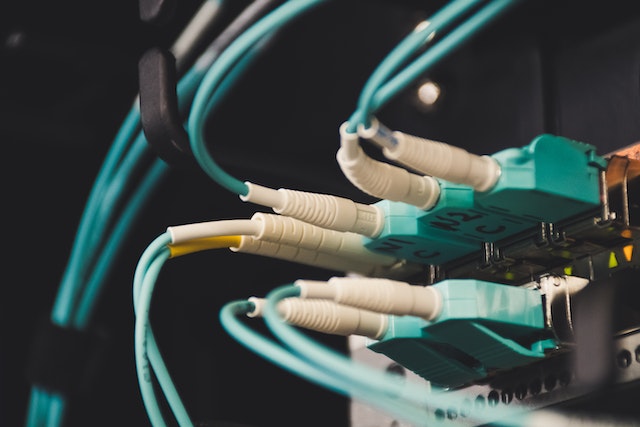
We are all aware of how essential each piece of musical equipment is to delivering high-caliber audio and a captivating listening experience. The coaxial speaker cable is the best speaker wire for sending high-quality audio signals between audio components and speakers. Due to their distinctive construction and layout, these cables reduce signal loss and disturbance, enhancing music clarity and fidelity.
This post will go over the features, benefits, and things to think about when using coaxial speaker wires with your current setup.
What Is A Coaxial Speaker Cable?
To allow for the smooth transmission of radio frequency (RF) signals, coaxial cables are frequently used. These speaker lines effectively transmit digital impulses over analog. Through a coaxial connection, they can handle high-frequency digital transfers and lower audio output ranging from around 20 kHz to 300 GHz. Additionally, when contrasted with traditional audio connections, these cables seem to provide better digital data bandwidth and longer lifespan.
How Is A Coaxial Cable Made?
Coaxial cables come in many different varieties with distinctive designs for a wide range of applications, but they all have four basic elements. The following elements are ordered from outermost to innermost in order of appearance:
1. Core Conductor
This component transmits the signal and grounds the cable’s electrical wiring, making it the active component. These are frequently made of copper, however, they are occasionally made of steel and wired with copper. An electrical isolator surrounds the core metal conductor.
2. Metal Shield
A coaxial cable made of coiled copper wire and aluminum foil is frequently found with two shields. This part shields the communication signal from radio wave distortion.
3. Plastic Jacket
The cable’s outer plastic jacket, which is typically constructed of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), protects the inside components that regulate transmission and noise cancellation.
4. Dielectric Insulator
The insulator separates the cable’s center from the copper barrier. The type of insulators incorporated into the core wire can range from foam plastic to solid plastic (or) air spacers, based on the form of coaxial cables. It also contains a PVC-coated sheath, which makes the insulator’s outer layer flexible.
What Sets It Apart From Digital Coaxial Cables?
People who are unfamiliar with various speaker wiring could find coax cable and digital coax cable confusing. So let’s examine the differences between a digital coax cable and a regular coax cable.
Additionally, they are created similarly to accomplish the same goal. The digital coax cables have a metallic shield, a plastic sheath, and an insulation-covered center wire.
Cable boxes, cable TV modems, runners, satellites, radios, TV antennas, home speakers, premium speakers, Blu-ray players, and many other devices can all be linked to coaxial digital audio cables.
Because they can accommodate a wide range of electromagnetic rates, music lovers prefer to use digital music coaxial cables. While traditional coaxial wires are capable of handling higher-quality, multiple channels audio formats, digital coaxial audio cables cannot.
Coaxial Speaker Cable Types:
To accommodate a variety of audio system requirements, coaxial speaker wires are generically categorized into several varieties depending on RG standards, features, characteristics, and construction.
1. Coaxial Hardline Cable:
The core conductor and shield of hardline coaxial cables are constructed from premium materials like copper, silver, aluminum, or steel.
For optimal efficiency, these cables typically incorporate a dielectric buffer, such as polyethylene foam (or) compressed nitrogen.
They are perfect for radio broadcasts and military communications since they are built to send powerful signals over expanses of as far as 400 feet.
2. Coaxial Subwoofer Cable:
To produce crisper and more dramatic sound, subwoofer coaxial cables use solid copper core bass conductors that are wrapped in a second wire network.
These cables improve sound quality, especially in the low-frequency ranges, by having RCA connectors on both ends.
They are specially made to link subwoofers to audio gear. Indeed, they contribute to the lifelike, immersive aural experiences that make films and TV shows come to life.
3. Coaxial Cables That Are Flexible:
Braided cables known as flexible coaxial cables constantly maintain weak signals, provide interference protection, and improve communication.
Numerous audio applications benefit from flexible coaxial cables’ simplicity of use and flexibility in installation.
Due to their flexibility and ability to bend and maneuver around curves, these cables serve in applications where space is at a premium or when flexible cable routing is crucial.
Additionally, they make linking audio equipment simple and flexible, making them suitable for a variety of applications including home theatre setups, studio settings, and high-end audio setups.
4. Micro Coaxial Speaker Cable:
Small speaker cables called micro-coaxial cables offer exceptional signal integrity and trustworthy high-voltage signal transfer.
Electronics, internet access, medical devices, and aviation are just a few of the industries that frequently use these connections.
These micro coaxial cables were created with applications demanding small and light cable solutions in mind.
For precise transfer of signals, you can frequently find them in tiny electronic components like board-level sensors, cameras, and antennae.
5. Stiff Coaxial Cables:
Rigid coaxial cables originate with a solid core conductor enclosed in insulation, a metal shield, and an outer jacket added later.
The metal shield preserves signal integrity and guards against electromagnetic interference (EMI).
They don’t flex and remain solid because they comprise sturdy material.
They function in applications where precise and dependable data transport over long distances is essential.
6. Semi-Rigid Coaxial Cables:
Like pipes, semi-rigid coaxial cables are strong and durable. A secondary conductor is provided by the outer metallic covering, and the metal layers aid in preserving a constant impedance along the cable’s whole length.
Low signal loss and interference are the result of these cables’ outstanding signal integrity and shielding.
They are frequently employed in industries including telecommunications, aviation, and defense where high-frequency tasks necessitate outstanding electrical efficiency, mechanical stability, and precise signal transmission.
7. Formable Cable:
Coaxial wires that are easily moldable or shapeable by hand are known as formable coaxial cables. This means that these cables can be bent, twisted, or otherwise formed to accommodate unique installation requirements or challenging routing routes.
When rigid (or semi-rigid) coaxial cables cannot be utilized, formable coaxial cables are frequently employed in the telecommunications, robotics, aerospace, and automobile industries.
8. Triplex Cable:
A core conductor, an inner shield, and an outer shield are the three circular layers that make up triaxial cable, also referred to as triax cable. Two conductors serve as a ground and return line, while one conductor carries the primary signal.
The electromagnetic interference (EMI) protection, decreased noise, and communication quality are all improved by the triple-layered design.
They are extensively employed in signal transmission applications like instruments, expert audio gear, and surveillance video devices.
9. Coaxial Radiating Cable:
Radiating feeder or leaky coaxial cable are common names for radiating coaxial cable. These cables are special since they were created to function as antennas and transmission lines at the same time.
The exterior conductor of these cables has been purposely given slots (or gaps), and they all produce electromagnetic radiation.
They are utilized in buildings, tunnels, and other subterranean and underground constructions where wireless coverage needs to be improved.
10. teeny Coaxial Cables:
Miniature coaxial cables are lightweight, flexible, thin wires that offer the advantages of conventional coaxial cables while taking up less room.
They are used in applications with less room because they are made for compact form factors, including consumer electronics, telecommunications equipment, medical devices, and vehicles.
Additionally, they are typically utilized to connect tiny components like cameras, sensors, antennas, and PCBs.
Coaxial Speaker Cable Dimensions:
For a variety of uses, coaxial cables are produced in a variety of sizes. These are some of the most typical cable sizes.
1. RG-6 Coaxial Cable:
RG-6 coaxial cables can transfer high-definition films and data without any signal loss because of their 75 impedance, 6.86–7.57 mm outer diameter range, and 1.024 mm core diameter.
It coaxial wire is frequently terminated using F-type links, which offers a reliable connection. Cable television sets satellite radio, internet access, and video monitoring equipment all require coaxial connections.
Long cable runs are ideal for RG-6 coaxial cables because they enable effective signal transmission over great distances.
2. RG-7 Coaxial Cable:
High-quality video and data transmission with signal integrity is possible using RG-7 coaxial cables, which have a resistance of 75 ohms and a core diameter of 1.3 mm.
An effective and long-lasting connection is made by terminating RG-7 coaxial wire with F-type adapters. These coaxial wires are also utilized by modems, television cables, and satellite TV.
3. RG-8 Coaxial Cable:
In order to transmit high-frequency digital signals, RG-8 coaxial cables have an impedance of 50 ohms and an inner diameter that ranges from 1.47 mm to 2.17 mm.
Since it is a perfect fit for a variety of transmitter antennas and radio transmitters, RG-8 coaxial cables are frequently utilized for radio signals.
4. RG-11 Cable Coaxial:
Excellent data transfer requires RG-11 coaxial cables, which have an impedance of 75 and a 1.63 mm core diameter and 10.5 mm outer diameter.
These robust coaxial cables can support and handle a wide range of frequencies up to 3 GHz or higher for trustworthy digital transfers over great distances.
They are employed in broadcast systems that demand high performance and low signal loss, such as satellite transmissions, massive cable TV network distribution, and speed web traffic.
5. Rg-56 Coaxial Cable:
For the transmission of high-voltage signals, RG-56 coaxial cables have a core diameter of 1.49 mm, an outside diameter of 7.82 mm, and an impedance of 48.
They are frequently employed in high-voltage uses and can tolerate voltages of up to 8000 v.
6. Rg-58 Coaxial Cable:
For efficient communication, RG-58 coaxial cables have a resistance of 50, a core diameter of 0.81 mm, and an outside diameter of 5 mm.
They are perfect for amateur radio, broadcasting, and nuclear electronic devices.
7. RG-59 Coaxial Cable:
In order to transmit a small amount of data without signal loss, RG-59 coaxial cables have a 0.64 mm core diameter, a 6.1 mm outer diameter, and an impedance of 75.
They are mainly utilized for lower-frequency video and audio applications, including CCTV systems, recording setups, and older composite video links.
8. Rg-60 Coaxial Cable:
For the transmission of high-voltage signals, RG-60 coaxial cables have a core diameter of 1.024 mm, an outside diameter of 10.8 mm, and an impedance of 50.
They are frequently built to manage fast speeds services like HD cable TV, rapid broadband, etc.
Coaxial Speaker Cable Advantages And Drawbacks:
As they transmit radio waves with less interference, coaxial cables are a great choice for sending the signal from your receiver (or) amplifier to your speakers. The list of benefits and drawbacks of coax cables is provided below.
Advantages:
- Higher transmission speeds are used for high-quality audio signals.
- These cables are incredibly durable and easy to set up.
- Excellent shielding against noise or interference from other broadcasts was built into the design.
- delivers superior sound quality and dependable performance across shorter distances.
- Because of their exceptional longevity and capacity to produce outstanding digital audio, they are frequently employed in professional settings.
- They offer excellent value without sacrificing the quality of the video and audio transmission.
- Coaxial cables are flexible and can be used in a wide range of industries and situations, including data networking, home entertainment systems, security systems, and TV and radio transmission.
Disadvantages:
- Longer lines might cause signal loss.
- Since coax cables are bigger, heavier, and less flexible, they are more challenging to conceal.
- extremely susceptible to disturbance from electromagnetic fields.
- only suitable for specific audio devices.
- It is more challenging to accurately terminate or end.
- Coaxial setups cannot support well-liked audio formats like DTS-HD Master Audio.
How Do I Select the Correct Coaxial Speaker Cable?
Here are a few key criteria to bear in mind while choosing a coaxial speaker wire.
1. Cable Gauge:
In most cases, a cable’s gauge relates to the wire’s thickness (or diameter). Higher power levels can be supported by thicker cables as they have less resistance to them.
In general, smaller gauge cables, like those with gauges of 12 or 14, are advised for speaker systems with higher power outputs, whereas bigger gauge cables, like those with gauges of 16 or 18, can be used for speaker systems with lower power outputs.
2. Cable Composition:
To ensure optimal signal transfer and endurance, pick high-quality wires. However, due to its outstanding conductivity properties, copper is frequently utilized for speaker cables. Additionally, use cables with the correct shielding and insulating to avoid signal interference and maintain the integrity of the transmission.
3. Cable Length:
Measure the distance first, then decide how much wire you’ll need for your speaker system. Make sure the wire is not unnecessarily long or short. Always link the sound source to the speakers with a cable that is long enough. Additionally, keep in mind that too-long cables could result in signal loss and poor audio quality.
4. Type Of Connector:
Select the appropriate type of connection for your speakers and audio devices. To ensure a secure and trustworthy connection, eliminate signal loss, and facilitate setup, make sure the connectors you choose are constructed of superior materials.
5. Budget:
Before buying the coax cables, determine your budget. Select a cable that works with your audio system and supports the necessary functions. However, there are several cables with a variety of functions that are priced reasonably.
6. Reviews:
Before buying the cables, we usually advise reading the reviews left by other users on various web platforms. These reviews will genuinely assist you in determining the performance of the cables and selecting the best option for your requirements.
Conclusion:
The coaxial speaker cable, which winds up, is a common part of audio gear used for speaker hookups, cable boxes, and other audio and video signal transmission. Radiofrequency (RF) signals can be sent using this type of electrical wire. The topic of coaxial speaker cables is finished. We hope that this article covered all the crucial details, including what they are, how they are categorized, their advantages, their limitations, and the variables that must be taken into account when selecting the best coax cable for your needs.
FAQs:
1. Is A Coaxial Cable Effective For Transmitting Audio?
Yes, a coaxial cable is effective for transmitting audio. Coax wires can be utilized as microphone cables in addition to regular speakers and subwoofers because of their capacity to create low frequencies with high noise ratios.
2. Is A Coax Cable Suitable For Use As A Subwoofer Cable?
Because of their enhanced insulation and reduced price, coaxial cables can be used as subwoofer cables over longer distances than 40 feet.
3. What Type Of Coaxial Wire Is Most Typical?
One of the most popular and widely used types of coaxial cables is the RG-6 coaxial wire. It is frequently used for fast internet access, cable TV structures, and satellite TV setups.
4. What Kind Of Coaxial Cables Are Utilized For Internet Connections?
The capacity and signal integrity needed for fast data transfer in cable internet and mobile devices arrives by RG-6 and RG-11 coaxial cables, which are frequently used for internet access.
5. Is There A Speaker Wire To The Coaxial Adaptor Available?
Yes, there are coaxial-to-speaker actually wire adapters available. They are equipped with speaker wire connections on one end and a coaxial input on the other. These converters are used to change a coaxial connection into an audio wire link.
Related Posts: