Customer Retention vs. Acquisition: Why Retention Wins Every Time

The e-commerce and SaaS business sectors continuously improve with the latest technologies. That is why brands are frequently involved in ...
Read moreSEO’s Compounding Returns: The Strategy That Keeps Giving

In this digital landscape, there are many businesses present online that are repeatedly striving for outstanding marketing strategies. Those strategies ...
Read moreFintechZoom.io: Connecting Finance with Technology

Technology has been changing the modern lifestyle significantly. Finance is a part of our life. To deal with money, we ...
Read moreSowix Online: The Best Platform on Ecommerce
Sowix Online presents a shopping platform sharing the scenario of retail. This platform for shopping is truly exceptional. You can ...
Read moreShannon Swanick TPO: The Tips for Creating Engagement in Website

The scenario of social media and digital marketing is changing. Shannon Swanick TPO will explore the scenario and offer important ...
Read moreMediaTek MT8788 vs Snapdragon 680 – which one is better?
Both MediaTek MT8788 and Snapdragon 680 are ARM-based mobile processors. The main area of their activities revolves around the Central ...
Read moreCorpenpelloz: Exploring The True Meaning in Modern Times

Corpenpelloz is a word with different meanings in modern times. Based on our negotiation, we discovered a new meaning. Those ...
Read moreA Complete Knowledge Of cflop-y44551/300

At present, computation capacity enhances the spirit of innovation. cflop-y44551/300 is a wonderful instrument for dealing with complex actions. It ...
Read moreTech TheBoringMagazine – Discover The Latest News on Technology

Our online world is changing rapidly. The technology has been progressing really fast. It has influenced all aspects of our ...
Read moreBetechit: The Best Platform on Technology

Technology is changing quite fast and it is beyond our imagination. It is really important to get updated news. You ...
Read moreShould I get R8 or R7 or Z50II? – Complete Analysis of Camera
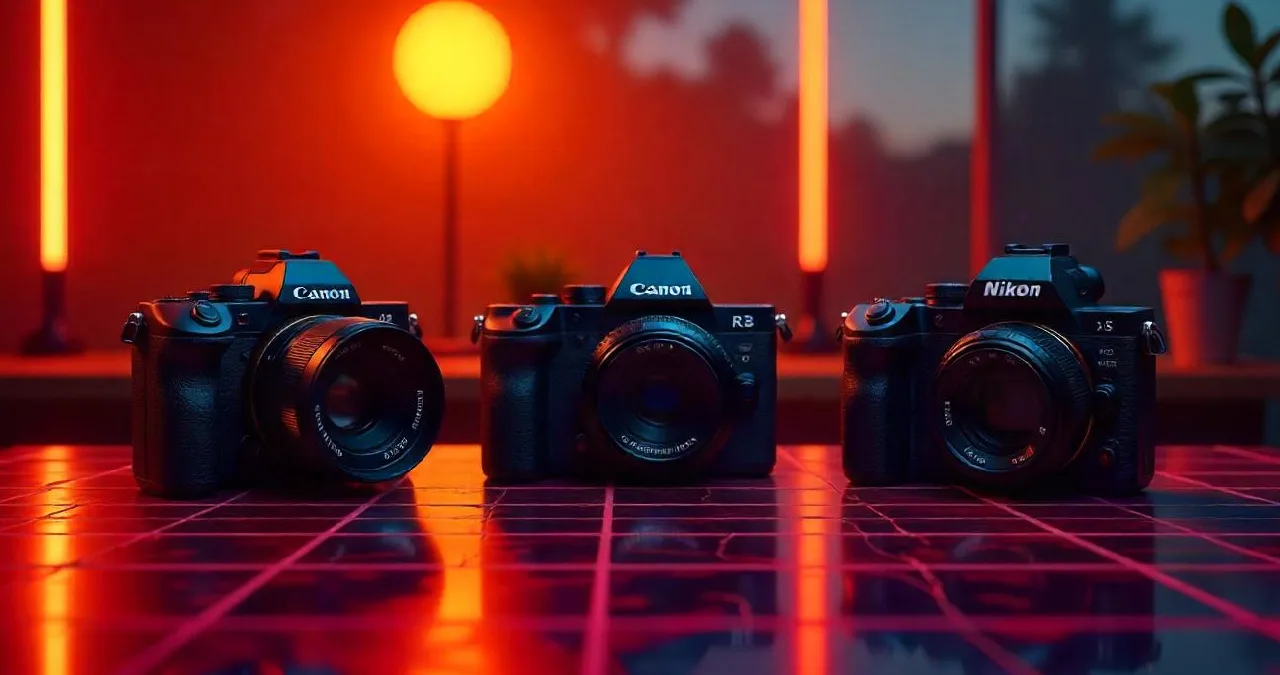

Nikon Z50ii, R7 and R8 of Canon are the three Camera types. If you are given the choice to select ...
Read more